User Input and Data Collection
Forms are how we collect data from users. They are ubiquitous on the web; we encounter forms everyday on most websites we visit. Login, job search, and creating a new email, are all forms.
 Forms always have a point - they capture something. Well designed forms allow for a more efficient capture of that something, and as
forms can be as simple as a two field login form, to a hundred field survey, applicant intake, or application form.
Forms always have a point - they capture something. Well designed forms allow for a more efficient capture of that something, and as
forms can be as simple as a two field login form, to a hundred field survey, applicant intake, or application form.
It is important to remember that as a form designer, we must guide our users through our form, so that they can quickly, and most
importantly (to us and our clients), accurately.
If a form leaves a user asking questions, relies on color only for required fields, does not allow for assistive technologies, and is not mobile first, users of that form might trust the company that authored the form a little less.
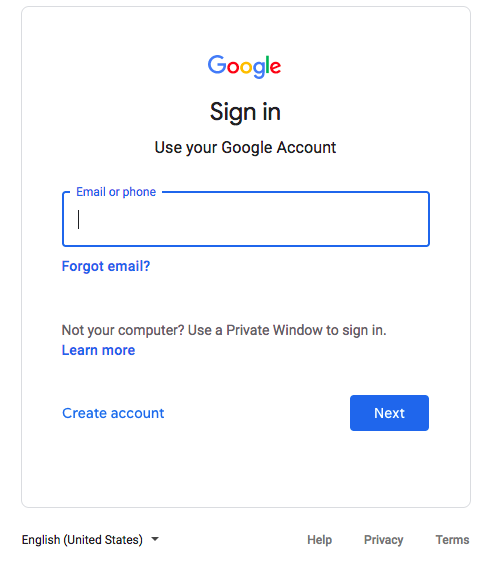
This sign in form is asking for login name. The form guides the user to the Next button which is highlighted in a solid color. The secondary option is
to create an account, with other options avaliable to the user, such as privacy, designed to seem less important or required.
See: WC3 - Forms